X2 Handover in LTE: A Tutorial
December 22, 2019


Content Monetization with Cable TV and Satellite Operators
December 26, 20195G Handover
4G LTE handover was called X2 and S1, in 5G NR are called XN and N2
5G has come close to standardization with many news from Verizon and T-Mobile regarding deployments and acquisitions specially with NOKIA.
- ♦ NOKIA inks deal with T-Mobile for $3.5B (Press Release)
- ♦ Verizon and Nokia competete 5G NR Mobility Call (Press Release)


4G LTE Systems
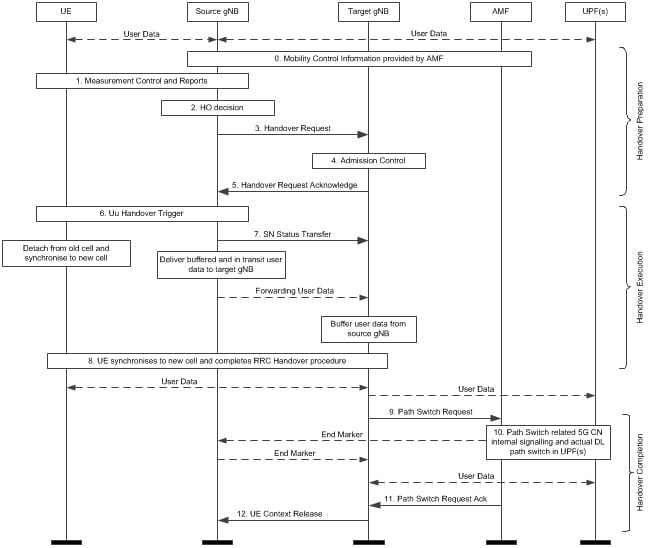
In the 4G LTE System, we would have an ENodeB, MME, S-GW, PDN-GW, as common elements of the network, hence the X2 and S1 interfaces were used for handover.




In this design, X2 handover facilitates handoff between eNodeBs and relies on the MME for S1-AP handoff only.
In 5G, things have changed a bit:
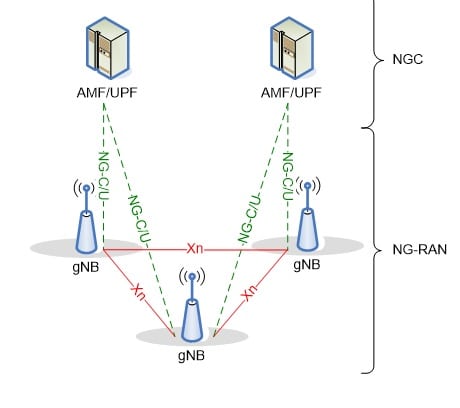

In comparison, UEs are the same, different radios, on one end LTE, and into the future a 5G radio.
What are the main actors for handover on LTE
- ♠ eNodeB – or the Base Station, contains the RF and all IP-level connectivity to the MME/S-GW/PDN-GW to create and maintain connectivity between the RF and EPC-Bearer or Tunnels to the outside world.
- ♠ S-GW: Refers to a component that connects the eNodeB with the PDN-GW and is usually a router that sends the tunnel to the PDN-GW with data from the eNodeB or the UE
- ♠ PDN-GW: Functions as the anchor or the home of the network, is the main NAT/Routing GW to the internet and keeps track of all tunnels for each UE on the network, and knows how to forward packets to the UEs.
- ♠ MME: The Mobility Management Entity, handles mobility in general, required for the S1-AP handover, and handles many mobility functions coordinating with the PDN-GW/S-GWs.
There are multiple specifications related to handover on LTE and defined by ETSI/3GPP organizations.